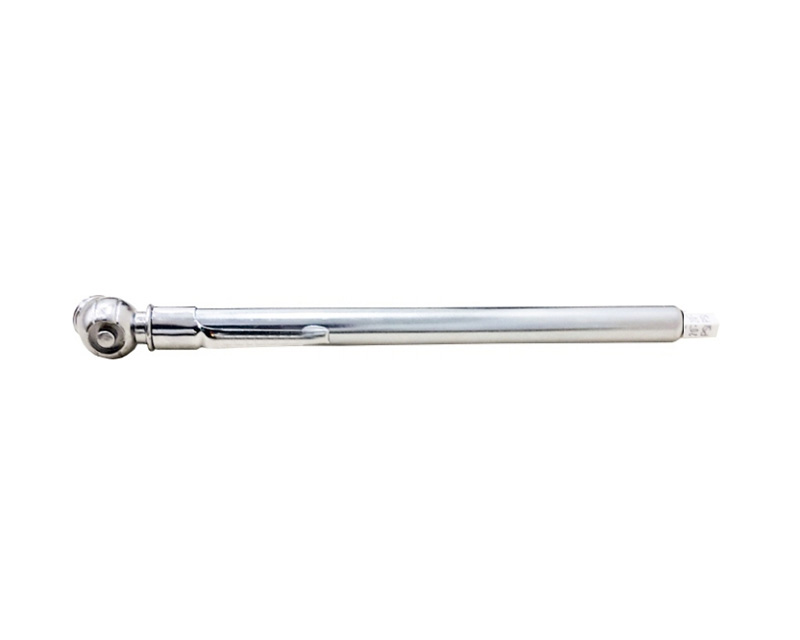
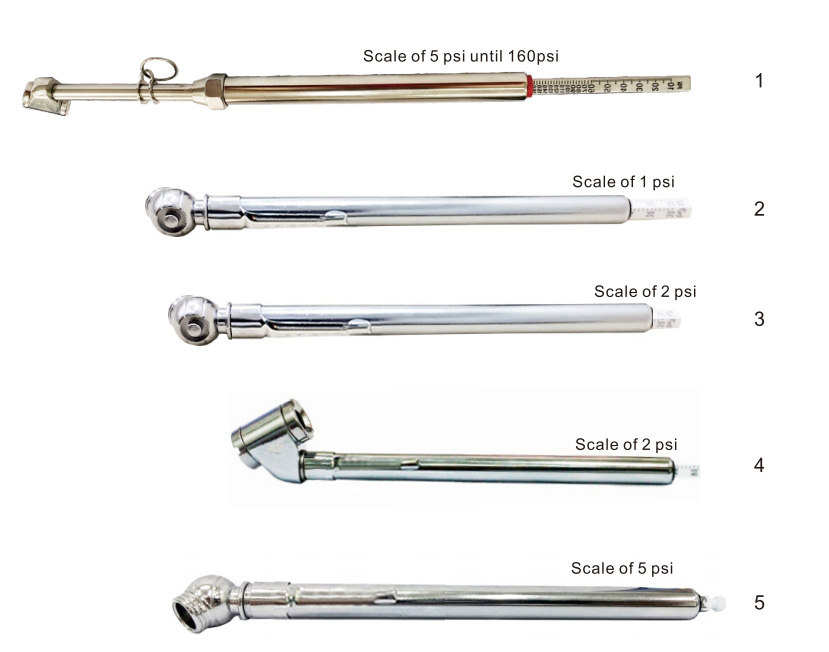
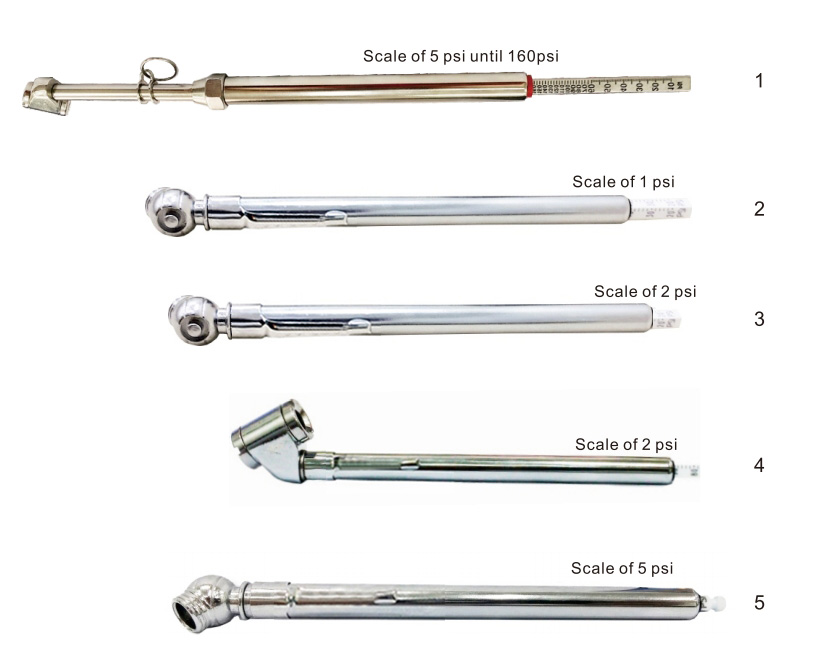
R8100C
Characteristics & Applications of Barometers
A barometer is an instrument designed to measure the pressure of gases and liquids. It is one of the most commonly used devices in modern industry and laboratories. By detecting the deformation of a sensor caused by the medium under test, the barometer obtains an accurate pressure reading. Its features and applications span a wide range of fields, detailed below.
Key Characteristics of Barometers
Wide Measurement Range: Capable of measuring pressures of various gases and liquids, covering common ranges and meeting the demands of diverse operating environments.
High Accuracy: Offers high measurement precision—often within one percent or better—delivering reliable and repeatable results.
Simple Structure: Typically consists of a case, dial, pointer, and sensor, resulting in a compact design that is easy to install and operate.
Easy Maintenance: Requires only periodic calibration and inspection, ensuring a long service life with minimal upkeep.
Cost-Effective: Moderately priced with low overall cost of ownership, making it suitable for widespread deployment.
Primary Application Areas
Industrial Applications: Widely used in petrochemical, pharmaceutical, food-processing, automotive manufacturing, and other industries to monitor gas and liquid pressures in equipment and pipelines, ensuring smooth production processes.
Laboratory Applications: Essential for pressure measurement in chemical, physical, and biological experiments—e.g., controlling gas flow rates and monitoring internal vessel pressures.
HVAC & Refrigeration: Commonly employed to measure refrigerant pressures, guaranteeing the proper operation of air-conditioning and refrigeration systems.
Pressure Control Systems: Integral to pneumatic and hydraulic systems for real-time monitoring and regulation of system pressure.